Introduction
The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized asset tracking, providing innovative solutions to monitor and manage resources effectively. Among the various connectivity technologies available, LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) stands out as an optimal choice for factories, harbors, campuses, parking lots, hospitals, and even nationwide tracking projects. This paper explores the advantages of LoRaWAN, particularly in the context of a parking lot, factory, warehouse, or livestock tracking, and demonstrates why it is the best connectivity technology for such endeavors.
Advantages of LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN, Long-Range Coverage
LoRaWAN technology is renowned for its extensive coverage capabilities, spanning several kilometers. This is particularly beneficial for a parking lot where cars may be spread across large areas, including buildings, open spaces, and remote locations. The ability to cover long distances ensures that tracking devices can communicate effectively with gateways, regardless of their location.
Lansitec badge tracker communication distance:
· 5km @SF9 with a few buildings and woods between the gateway and tracker.
· 19km @SF9. The gateway is on a 30m high building on the coast, and the tracker is on a ship
Solar Bluetooth gateway:
· 3km @SF9 with a few buildings and woods between the gateway and tracker.
The distance can be further by increasing the SF to 10, 11, or 12.
To know more about LoRaWAN coverage, please refer to “What are the factors affecting LoRaWAN range in IoT?”
The long-range coverage feature makes LoRaWAN ideal for the following tracking projects:
· Vehicle and key tracking in dealers’ parking lots
· Offshore fishman and worker tracking
LoRaWAN, Low Power Consumption
One of the significant advantages of LoRaWAN is its low power consumption. Devices using LoRaWAN can operate for extended periods on a single battery charge or one small non-chargeable battery, which is crucial for tracking applications where frequent battery replacements would be impractical. This feature reduces maintenance costs and ensures continuous monitoring of personnel, cars, and assets without interruption.
The low TX and RX current compared with the cellular network also reduces the requirement for battery output, so we have more battery options.
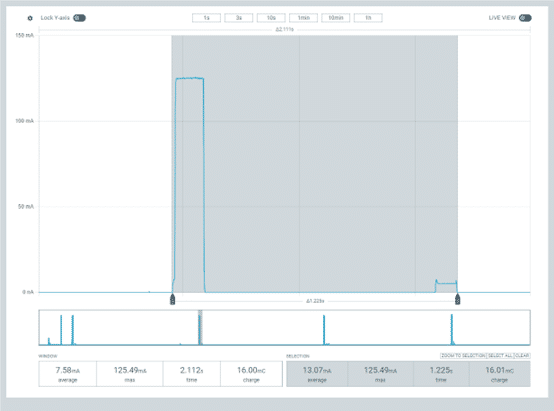
- MCU: nRF52832
- LoRa RF: SX1262
- SF9
- Data size: 9 bytes
- Confirmed Message
- System Average TX Current: 110.78mA
- System Average RX Current: 4.97mA
- Total power consumption: 16.01 mC, 0.00445 mAh
LoRaWAN, Cost-Effectiveness
LoRaWAN is an affordable solution for asset tracking. The technology does not require expensive infrastructure, making it accessible for all projects with limited budgets. It uses the ISM band, which is free to use worldwide so that everyone can build their own LPWAN.
LoRaWAN has low operational costs, such as minimal battery replacements, various LoRaWAN gateways and network servers (NS) at different costs, and low data transmission fees, further enhancing its cost-effectiveness. Some LoRaWAN gateways have a built-in network server, which is ideal for small projects.
Also, we can find additional options for various suppliers, including device makers, NS, and APP providers in LoRa Alliance, to optimize our solution.
LoRaWAN Network Options
One of the significant benefits of LoRaWAN is that anyone can build their on-premise or cloud-based LoRaWAN network for different kinds of projects. In addition to a private network, users can tap into existing nationwide networks in countries like France, Belgium, and the Netherlands. These established networks provide comprehensive coverage and infrastructure for LoRaWAN-enabled devices.
For those seeking a more decentralized approach, Helium offers an intriguing alternative. Helium’s network operates on a global scale, relying on a distributed network of hotspots maintained by individual users. This decentralized model allows for broader coverage and greater flexibility, making it an attractive choice for IoT (Internet of Things) applications worldwide.
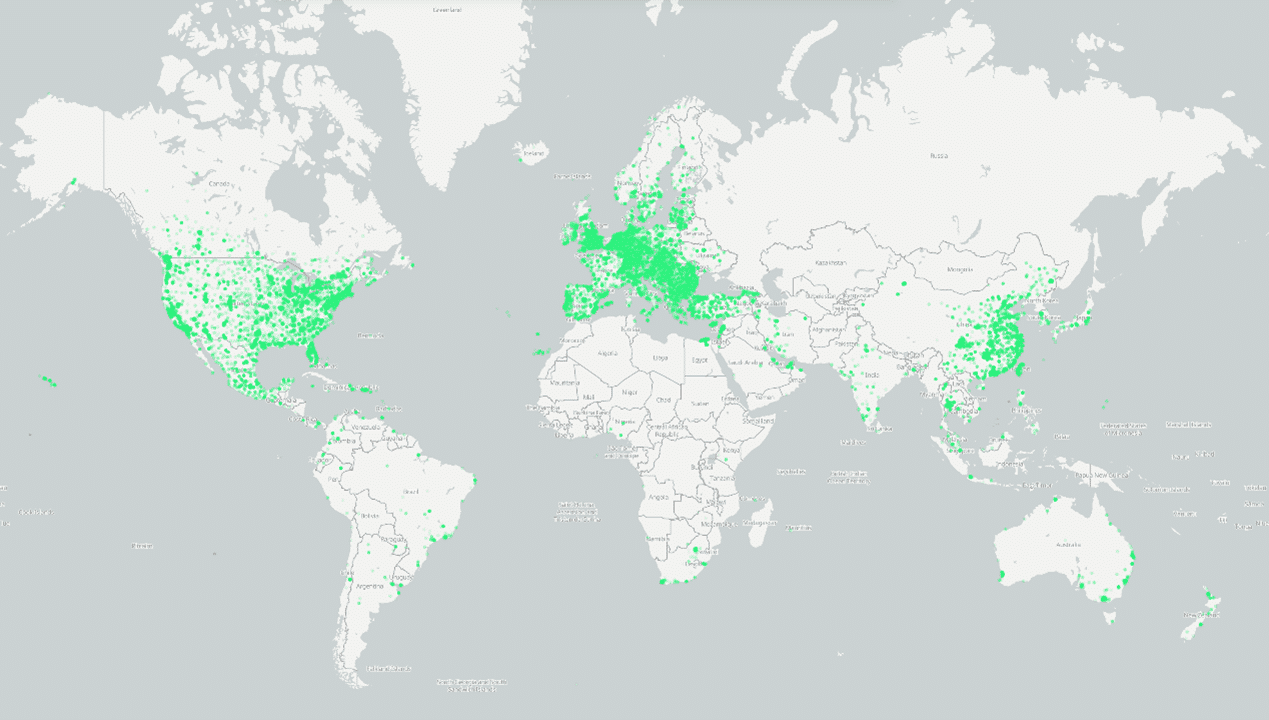
Satellite-based LoRaWAN communication offers another way to track live stock, vehicles and containers. It includes some unique features:
LoRaWAN Global Coverage: Satellite connectivity ensures that LoRaWAN devices can communicate from virtually anywhere on Earth, even in remote or rural areas with limited terrestrial network infrastructure.
LoRaWAN Scalability: LoRaWAN satellite networks can accommodate a large number of devices, making them suitable for large-scale IoT deployments.
LoRaWAN Cost-Effective: LoRaWAN satellite solutions often offer a more cost-effective alternative to traditional satellite communication technologies.
LoRaWAN Reliability: Satellite communication provides a high level of reliability and resilience, even in challenging environments.
Users can even use peer-to-peer communication (in addition to LoRaWAN) in cases where only a few devices and a simplified network are needed, such as a fisherman alert and tracking system.
So, the LoRaWAN network is flexible, and it can be as small as a ship to track sailers and fishermen, or nationwide to track containers, pallets, and rental assets.
LoRaWAN Network Capacity
The LoRaWAN network capacity is not an issue in most monitoring systems because the report frequency is low, from minutes to hours, or it may be event-triggered. However, in a tracking project, users want to track assets or personnel from every several seconds to minutes.
Example 1:
- GNSS Tracker: 750 pcs
- Report Interval: 5 minutes
- Data size: 9 bytes
- SF7, LoRaWAN gateway capacity rate is 3.6%
- SF8, LoRaWAN gateway capacity rate is 7%
- SF9, LoRaWAN gateway capacity rate is 14%
To maximize the network capacity and minimize package loss, it is better to keep the capacity rate lower than 15%.
Example 2:
- GNSS Tracker: 50 pcs
- Report Interval: 15s
- Data size: 9 bytes
- SF7, LoRaWAN gateway capacity rate is 5%
- SF8, LoRaWAN gateway capacity rate is 10%
- SF9, LoRaWAN gateway capacity rate is 20%
For detailed network capacity evaluation, please refer to our “8 Channel LoRaWAN Network Capacity Evaluation”, PN: 511-00054.
As we can tell from example 1 and 2, the capacity of a LoRaWAN network is a function of its gateway density. Spreading Factor (SF), data size, and bandwidth determine the capacity of a one-gateway network. We can also expand the network capacity by adding more communication channels: from 8 to 16 uplink channels in EU868 or from 8 to 16 or more (up to 64) in US915, AU915 and CN470. The capacity can also be increased by adding more LoRaWAN gateways.
For Bluetooth gateways and sensors that are static, using an adaptive data rate (ADR) mechanism is essential. The main goal of ADR is to save the battery power of the LoRaWAN end nodes. Having the end nodes closest to a gateway transmits using the lowest spreading factor minimizes their time on air and prolongs their battery life. More distant sensors transmit at a higher spreading factor. A trade-off is made between battery power and distance, given that a higher spreading factor allows for a gateway to connect to devices that are further away
However, for a tracker that is mobile, it is better to use a fixed data rate to save power while it roams at different distances to the LoRaWAN gateway. The fixed data rate also maintains stable communication for a mobile device, i.e., trackers.
LoRaWAN Roaming and Mobility
In LoRaWAN, end nodes are not connected to a specific gateway. Instead, data transmitted by a node is typically received by multiple gateways and forwarded to the central network server, where the messages are verified and forwarded securely to the APP. Intelligence and complexity are transferred to the network servers that manage the network and will filter redundant packets received, perform security checks, schedule acknowledgments through the optimal gateway, perform adaptive data rates, and more. If the node is mobile or moving, there is no need to pass control from gateway to gateway, which is a key feature that allows the asset tracking application.
LoRaWAN High Security
Security is a paramount concern in any tracking project, especially when dealing with sensitive data. LoRaWAN employs robust encryption standards, ie. AES-128, to ensure that data transmitted between devices and gateways is secure and protected from unauthorized access. This high level of security is essential for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of tracking information.
LoRaWAN Payload size, Data Rate and Latency
LoRaWAN offers a versatile data transmission profile with a maximum application payload of 11-242 bytes (depending on the frequency band and spreading factor), data rates ranging from 255bps to 50kbps, and latency typically measured in seconds depending on the RECEIVE_DELAY setting). While these parameters may not always surpass NB-IoT, CAT-M, or Cat-1 in every aspect, they are well-suited for many tracking applications.
LoRaWAN Case Studies and Practical Implementations
Cars and Keys in Dealers’ Parking Lot
Lansitec B-Mobile® Solution combines Bluetooth beacons, and Bluetooth gateway with LoRaWAN to provide seamless cars and keys tracking capabilities. Here’s how it works:
Bluetooth Beacons: These small devices can be attached to keys and hang on the rear-view mirrors. They continuously advertise their presence.
Bluetooth Gateways: Strategically placed Bluetooth gateways detect these beacons when they come into range. These gateways then transmit the beacon data (major, minor, battery status, and RSSI) over LoRaWAN networks.
LoRaWAN: Offers wide-range and low-power tracking. With up to 5 km range in urban areas and over 20 km in rural environments, LoRaWAN gateways cover large areas. The Chirp Spread Spectrum modulation ensures resilience to interference.
Benefits
Enhanced Customer Experience: Real-time tracking improves customer service during audits and interactions.
Bluetooth Beacon Long Battery Life: Bluetooth beacons can last over 5 years, ensuring persistent tracking.
Solar Bluetooth Gateway: The Bluetooth receiving on the Bluetooth gateway can continuously receive nearby beacons and report to a LoRaWAN immediately. The low power consumption enables the Bluetooth gateway to be free from maintenance.

Container Tracking
Users can deploy LoRaWAN gateways on ports between islands, factories, and warehousing to provide seamless connectivity.
Container tracking: The Lansitec LoRaWAN Container Tracker provides real-time visibility during transit between islands. You’ll always know where your containers are, whether on ships, trucks, or in storage yards.
Attach these trackers to pallets, machinery, or other assets in factories and warehouses. Monitor movement, optimize workflows, and prevent loss or theft.
Machine Usage Monitoring: Keep track of equipment usage patterns. Identify idle machinery or detect anomalies in operation.
Asset Management: Whether its tools, spare parts, or valuable inventory, this tracker streamlines asset management with Bluetooth and transits the information over LoRaWAN.
Worker Tracking
Lansitec badge tracker and helmet sensor can be used to track workers on a construction site, oil platform, or wind power plant on the sea.
Badge Tracker
Lansitec badge tracker is designed based on GNSS, Bluetooth 5.0 and LoRa technology. It supports indoor and outdoor tracking. The badge is mainly used for personnel and asset management.
Its built-in 3-axis accelerator could be used for determining the motion status of the terminal. Therefore, it can help save battery and enhance user experience.

Helmet Sensor
Lansitec Helmet Sensor is designed based on GNSS, Bluetooth5.0 and LoRaWAN technology. It supports indoor and outdoor tracking.
It supports various features which contribute to easy management in industrial settings. Its built-in 3-axis accelerator could be used for determining the motion status of the terminal. Therefore, it can help save battery and enhance user experience.
UWB High Precision Tracking
LoRaWAN can be used for data synchronization and transmission in a UWB high-precision tracking system. Anchors deployed 20~30m away from each other can be battery-powered for more than 5 years with the benefit of the low power consumption of LoRaWAN. Trackers with LoRaWAN and UWB forward the distance information to a LoRaWAN gateway for the server to calculate its position.
In this LoRaWAN-based UWB tracking solution, both anchors and trackers are battery-powered, significantly reducing the deployment maintenance effort.
Do not hesitate to get in touch with us to get further information on the LoRaWAN-based UWB tracking solution.
Conclusion
LoRaWAN emerges as the best connectivity technology for a regional tracking project due to its long-range coverage, low power consumption, cost-effectiveness, and high security. By leveraging LoRaWAN, parking lots, seaports, hospitals, and construction sites can effectively monitor and manage their assets, ensuring enhanced security and operational efficiency.








